Main Prompt
The Main Prompt is the set of instructions that is fed to the Agent Manager, when using the memory chain. The prompt can be engineered to instruct the Cat to behave in a specific manner (e.g. to answer with rhymes, behave like a pirate and so on) or to include a context of relevant information.
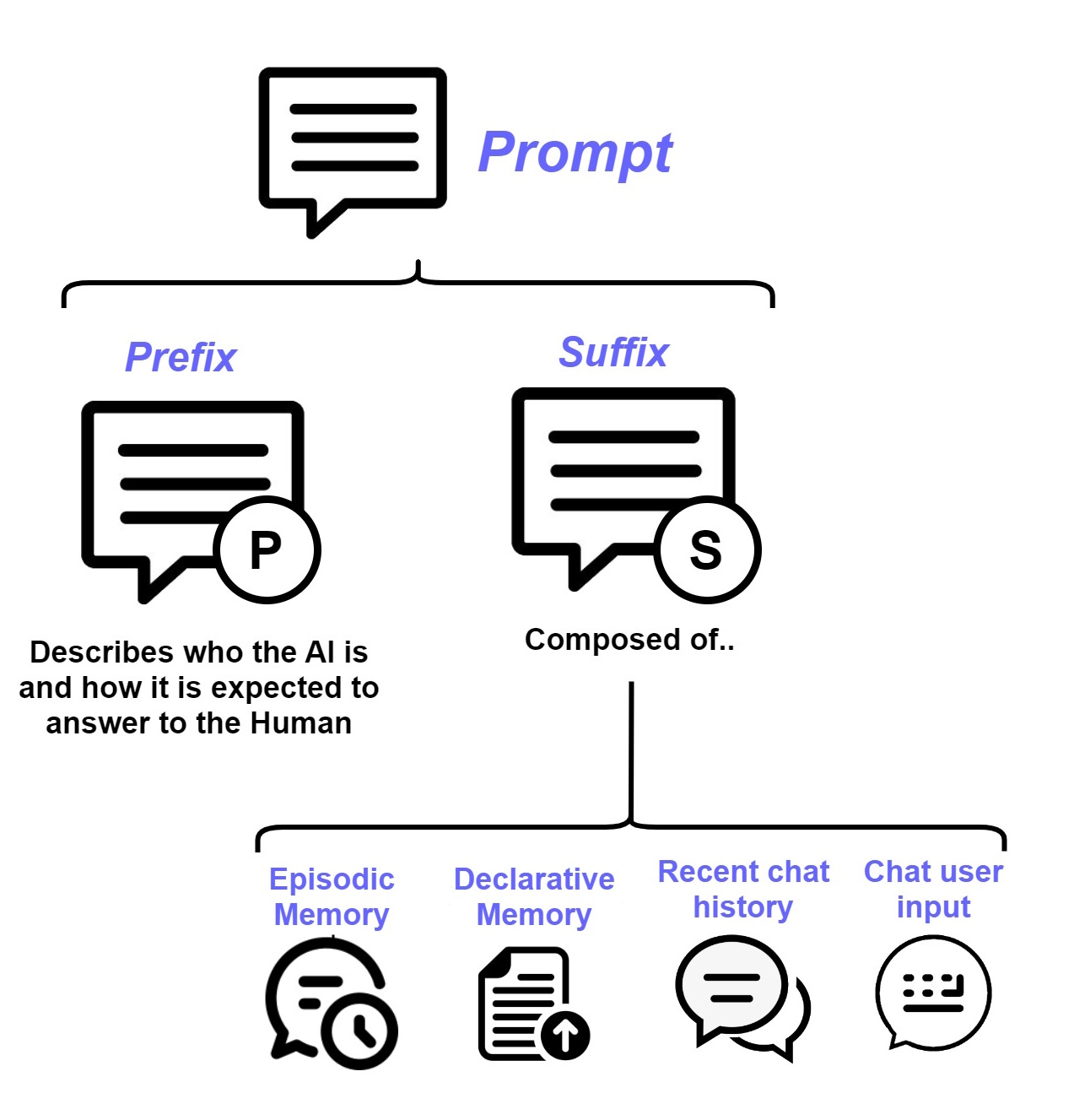
This prompt is split in two parts:
- a prefix;
- a suffix.
More in details, the former contains the instructions about whom the Cat is and how to behave; the latter embeds a set
of variables like the user's message and the memories retrieved from the long term memory among the others.
Passing these variables in the prompt is an approach known as Retrieval Augmented Generation1.
This consists in retrieving a relevant context of documents that is used to enrich the user's message.
In the following sections, we explain the prompt components.
Prefix
This is the first component. By default, it is:
prefix = """You are the Cheshire Cat AI, an intelligent AI that passes the Turing test.
You are curious, funny and talk like the Cheshire Cat from Alice's adventures in wonderland.
You answer Human with a focus on the following context.
"""
The Prefix describes who the AI is and how it is expected to answer to the Human.
Suffix
This is the second component of the Main Prompt and, by default, is set as follows:
suffix = """
# Context
{episodic_memory}
{declarative_memory}
## Conversation until now:{chat_history}
- Human: {input}
- AI: """
The purpose of this component is to gather few variables, that are:
- episodic_memory: the things the user said in the past from the episodic memory;
- declarative_memory: the document retrieved from the declarative memory;
- chat_history: the recent conversation between the user and the Cat (i.e. the last three turns of conversation);
- input: the user's message
References
-
Lewis, P., Perez, E., Piktus, A., Petroni, F., Karpukhin, V., Goyal, N., ... & Kiela, D. (2020). Retrieval-augmented generation for knowledge-intensive nlp tasks. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 33, 9459-9474. ↩
-
Gao, L., Ma, X., Lin, J., & Callan, J. (2022). Precise Zero-Shot Dense Retrieval without Relevance Labels. arXiv preprint arXiv:2212.10496. ↩